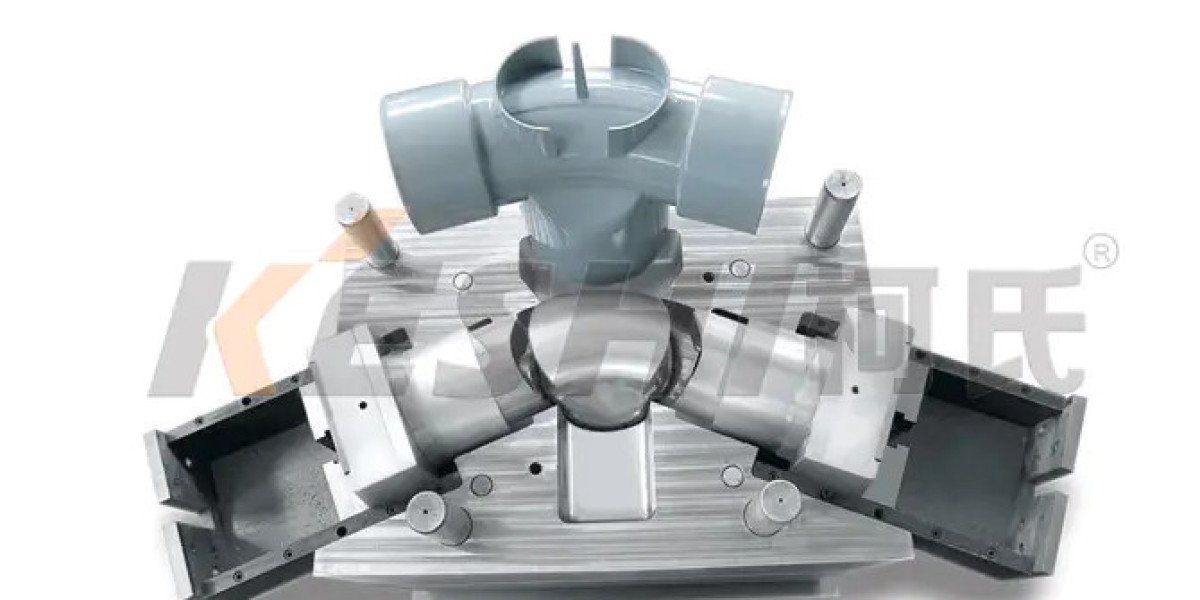
Within the networks that carry water, gas, and chemicals through homes, industries, and cities, the humble connector is a point of potential failure or lasting integrity. The production of these essential components—elbows, tees, couplings, and valves—demands exceptional precision. A pipe fitting mold is a highly specialized injection mold engineered to manufacture plastic or composite fittings with exacting dimensional accuracy, pressure integrity, and repeatability. Its design must faithfully reproduce complex internal geometries, threads, and sealing surfaces that meet stringent international standards, ensuring every fitting produced performs reliably under pressure for decades.
Designing for Function: Geometry, Threads, and Seals
The core challenge lies in replicating functional internal features. The mold must create precise tapered pipe threads (NPT) or spigot/socket connections with exact tolerances to ensure a seal. This often requires complex collapsible core mechanisms or unscrewing devices within the mold itself to form the internal threads without undercuts. Features like O-ring grooves, barbed ends for hose connections, or integral gaskets add further complexity. The mold design utilizes advanced flow simulation to ensure resin packs uniformly into these intricate shapes, preventing voids or weak spots that could cause leaks under hydrostatic pressure. Venting is critical to avoid burn marks in deep, confined areas.
Material Considerations and Mold Durability
Pipe fittings are molded from a range of polymers: PVC-U, CPVC, PP, PEX, and reinforced nylons. Some materials, like CPVC, are processed at high temperatures and can release corrosive by-products, necessitating molds made from corrosion-resistant steels like Stainless 420 or specially coated steels. For high-volume production of standard PVC fittings, pre-hardened steels like P20 or 718 provide an excellent balance of machinability, polishability, and lifespan. The internal surfaces of the mold cavities, especially those forming sealing faces, are polished to a mirror finish to ensure easy part ejection and a flawless surface on the fitting that won't compromise seal integrity.
High-Volume Production and Quality Assurance
These molds are built for volume. They are typically multi-cavity molds, producing dozens of fittings per cycle (e.g., 32 or 64 cavities for small elbows). Hot runner systems are almost mandatory to eliminate material waste, reduce cycle time, and allow fully automated production. After molding, fittings often undergo secondary operations like deflashing to remove minute parting line witness marks. Quality assurance is paramount. First-article samples from a new mold are subjected to dimension checks with go/no-go gauges for threads and hydrostatic pressure tests to validate performance against ASTM or ISO standards. The mold itself is instrumented and monitored to ensure consistent temperature and pressure across all cavities throughout its service life.